Shape Files and SQL Server
September 23, 2013
Over the last couple of weeks I have been doing a lot of work importing polygons into an SQL server database, using them for some data processing tasks and then exporting the results as KML for display. I thought it’d be worth a post to record how I did it.
Inserting polygons (or any other geometry type) from a shape file to the database can be done with the ogr2ogr tool which ships with the gdal libraries (and with Mapserver for Windows). I knocked up a little batch file to do it:
SET InputShapeFile="D:\Dropbox\Data\SingleView\Brazillian Polygons\BRA_adm3.shp"
SET SqlConnectionString="MSSQL:Server=tcp:yourserver.database.windows.net;Database=danTest;Uid=usernname@yourserver.database.windows.net;Pwd=yourpassword;"
SET TEMPFILE="D:\Dropbox\Data\Temp.shp"
SET OGR2OGR="C:\ms4w\tools\gdal-ogr\ogr2ogr.exe"
SET TABLENAME="TestPolygons"
%OGR2OGR% -overwrite -simplify 0.01 %TEMPFILE% %InputShapeFile% -progress
%OGR2OGR% -lco "SHPT=POLYGON" -f "MSSQLSpatial" %SqlConnectionString% %TEMPFILE% -nln %TABLENAME% -progress
The first ogr2ogr call is used to simplify the polygons. The value 0.01 is the minimum length of an edge (in degrees in this case) to be stored. Results of this command are pushed to a temporary shape file set. The second call to ogr2ogr pushes the polygons from the temp file up to a database in Windows Azure. The same code would work for a local SQL Server, you just need to tweak the connection string.
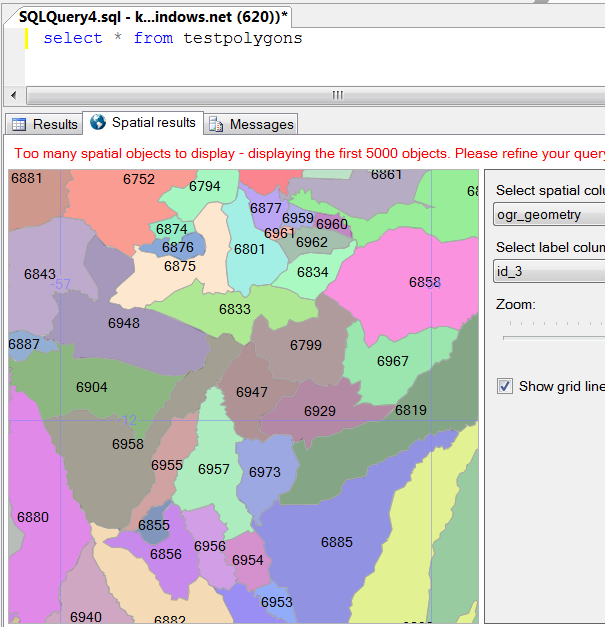
You can use SQL Server Management Studio to show the spatial results of your query, which is nice! Here I just did a “select * from testPolygons” to see the first 5000 polygons from my file.
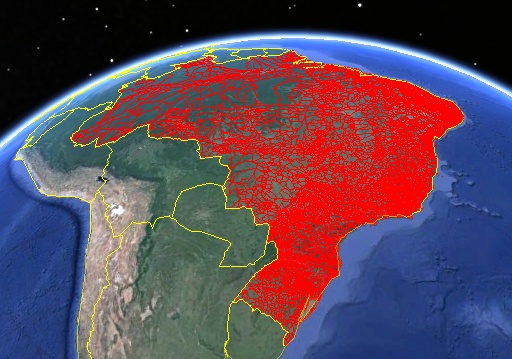
Sql Server contains all sorts of interesting data processing options, which I’ll look at another time. Here I’ll just skip to the final step - exporting the polygon data from the database to a local KML file.
SET KmlFile="D:\Dropbox\Data\Brazil.kml"
SET SqlConnectionString="MSSQL:Server=tcp:yourserver.database.windows.net;Database=danTest;Uid=usernname@yourserver.database.windows.net;Pwd=yourpassword;"
SET TEMPFILE="D:\Dropbox\Data\Temp.shp"
SET OGR2OGR="C:\ms4w\tools\gdal-ogr\ogr2ogr.exe"
SET SQL="select * from TestPolygons"
%OGR2OGR% -lco "SHPT=POLYGON" -f "KML" %KmlFile% -sql %SQL% %SqlConnectionString% -progress
Obviously you can make the SQL in that command as complex as you like.
Polygons here are from this site which allows you to download various polygon datasets for various countries.